Intel's Ivy Bridge CPU lineup
Intel has been busy as of late, with its new Sandy Bridge Extreme LGA-2011 platform launched two weeks ago, and the i7 Core 3960X taking the crown from the previous generation Core i7 980X as the fastest desktop processor available. The result was a foregone conclusion, given AMD's less than impressive top-of-the-line eight core "Bulldozer" FX-8150 performance when pitted against what are arguably two of Intel's best products in recent years -- the i5 Core 2500K and i7 Core 2600K.
With the Sandy Bridge Extreme launch out of the way, attention has now turned to the upcoming 22nm Ivy Bridge line-up, with full details of the entire i5 and i7 model lineup recently surfacing at CPU World.
Eleven new models are listed, covering the i5 and i7 range for mobile and desktop products. According to the site, the Ivy Bridge Core i7 family will feature 77, 65 and 45 Watt power envelopes, which correspond to suffix/"K", "S" and "T" processor numbers respectively. These are detailed in the charts below:

If the information above is correct, then it appears that most of the Ivy Bridge i5 processors will continue on from Sandy Bridge offering four physical cores, 6MB of L3 cache and no hyper-threading, except for the i5 3470T which is a dual core unit with two hyper-threaded cores.
Moving on to the i7 range, it appears they will continue in much the same way at their Sandy Bridge counterparts, running four physical cores with hyper-threading support, and 2MB more cache available. The new range topping Ivy Bridge part will launch as the i7 3770K, fully unlocked with a 3.5GHz clock speed, where as the "non-K" designated i7 3770 drops down 100MHz to 3.4GHz.
Therefore, in total consumers should see two unlocked, three mainstream, three mid-power level processors and three low power models which presumably will find their way into notebooks on the market once released -- with current estimates hinting at a launch date around April 2012.
===============
Five years ago Intel announced its ambitious tick-tock release cadence. We were doubtful that Intel could pull off such an aggressive schedule but with the exception of missing a few months here or there tick-tock has been a success. On years marked by a tick Intel introduces a new manufacturing process, while tock years keep manufacturing process the same and introduce a new microprocessor architecture. To date we've had three tocks (Conroe, Nehalem, Sandy Bridge) and two ticks (Penryn, Westmere). Sampling by the end of this year and shipping in the first half of next year will be Intel's third tick: Ivy Bridge.

Ivy Bridge (IVB) is the first chip to use Intel's 22nm tri-gate transistors, which will help scale frequency and reduce power consumption. As we already mentioned, mobile Ivy Bridge will be the first Intel CPU to bring four cores into a 35W TDP.
At a high level Ivy Bridge looks a lot like Sandy Bridge. It's still a monolithic die that features an integrated GPU. The entire die is built at 22nm, continuing Intel's march towards truly addressing integrated graphics performance. Ivy Bridge won't get rid of the need for a discrete GPU but, like Sandy Bridge, it is a step in the right direction.

Intel hasn't announced die size but transistor count has increased to approximately 1.4 billion (layout). This is up from 1.16 billion in Sandy Bridge, a 20.7% increase. With perfect scaling a 22nm Sandy Bridge die would be 47.3% the size of a 32nm die. Even with the increase in transistor count, it's a good bet that Ivy Bridge will be noticeably smaller than Sandy Bridge.
Motherboard & Chipset Support
Ivy Bridge is backwards compatible with existing LGA-1155 motherboards, although there will be a new chipset for Ivy Bridge and new motherboards to enable some features (e.g. PCI Express 3.0, native USB 3.0). The new chipset family falls under the 7-series banner. We'll see Z77, Z75, H77, Q77, Q75 and B75 available at or around launch.
| Chipset Comparison | ||||||||
| Z77 | Z75 | H77 | Z68 | P67 | H67 | |||
| CPU Support | IVB LGA-1155 | IVB LGA-1155 | IVB LGA-1155 | SNB/IVB LGA-1155 | SNB/IVB LGA-1155 | SNB/IVB LGA-1155 | ||
| CPU Overclocking | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | ||
| CPU PCIe Config | 1 x16 or 2 x8 or 1 x8 + 2 x4 PCIe 3.0 | 1 x16 or 2 x8 PCIe 3.0 | 1 x16 PCIe 3.0 | 1 x16 or 2 x8 or 1 x8 + 2 x4 PCIe 3.0 | 1 x16 or 2 x8 PCIe 3.0 | 1 x16 PCIe 3.0 | ||
| Processor Graphics Support | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | ||
| Intel SRT (SSD caching) | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | No | ||
| RAID Support | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||
| USB 2.0 Ports (3.0) | 14 (4) | 14 (4) | 14 (4) | 14 | 14 | 14 | ||
| SATA Total (Max Number of 6Gbps Ports) | 6 (2) | 6 (2) | 6 (2) | 6 (2) | 6 (2) | 6 (2) | ||
| PCIe Lanes | 8 (5GT/s) | 8 (5GT/s) | 8 (5GT/s) | 8 (5GT/s) | 8 (5GT/s) | 8 (5GT/s) | ||
As I mentioned above, Ivy Bridge finally supports USB 3.0 natively. The consumer 7-series chipsets feature 14 total USB ports, 4 of which are USB 3.0 capable. The CPU itself features 16 PCIe (1x16, 2x8 or 1x8 + 2x4) gen 3 lanes to be used for graphics and/or high performance IO. You will only see Gen 3 speeds on qualified motherboards. It's technically possible on 6-series motherboards but guaranteed on 7-series motherboards. The Z77 and H77 chipsets will support Intel's Smart Response Technology (SRT, aka SSD caching) which is a Z68 exclusive today.
SATA and chipset-attached PCIe slots haven't changed. Overclocking is supported on all Z-chipsets, while the H-chipset doesn't. All chipsets support Intel's HD Graphics, which is a departure from the Sandy Bridge mess where P67 didn't.
==========
معالجات
Ivy Bridge
ظهرت بالتفصيل من خلال
Slides
خاصة مسربة من
Intel
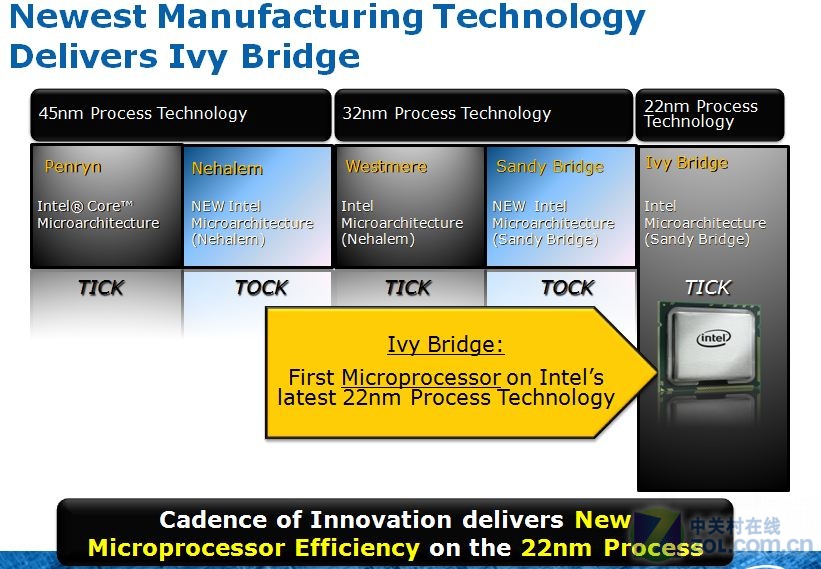
كما هو موضح هنا ان المعالجات ستأتى بدقة تصنيع
22nm

Maho Bay
و هو اسم الـ
Platform
الذى اطلق على معالجات
Ivy Bridge
اما
Sugar Bay
هو اسم الـ
Platform
المطلق على معالجات
Sandy Bridge
Sandy Bridge Chipset ---> Cougar Point 6 Series Family
Ivy Bridge Chipset ---> Panther Point 7 Series Family
Pin Compatible
بين الرقاقاتين
Ivy Bridge و Sandy Bridge +
استخدام نفس السوكيت
LGA 1155
ومعنى ذلك انه يوجد احتمالية كبيرة بان معالجات
Ivy Bridge
ستكون متوافقة مع لوحات
Sandy Bridge
الحالية
و لكن هذه المعلومة غير مؤكدة من
Intel
مميزات
Ivy Bridge:
USB 3.0 / DX11 / 3 Displays Support

دعم
16
lane
للـ
PCI-e
Intel Turbo Boost 2.0
دعم 1600
Mhz
للذاكرة
Quick Sync Video Technology
AVX acceleration

دعم
Rapid Storage Technology 11
SATA 6Gbs /SSD - HDD
Intel Vpro
Intel Identity Protection
2012 Intel SIPP
PCI-E Gen 2
او احتمالية
Gen 3
HDMI 1.4
الداعم للـ
3D
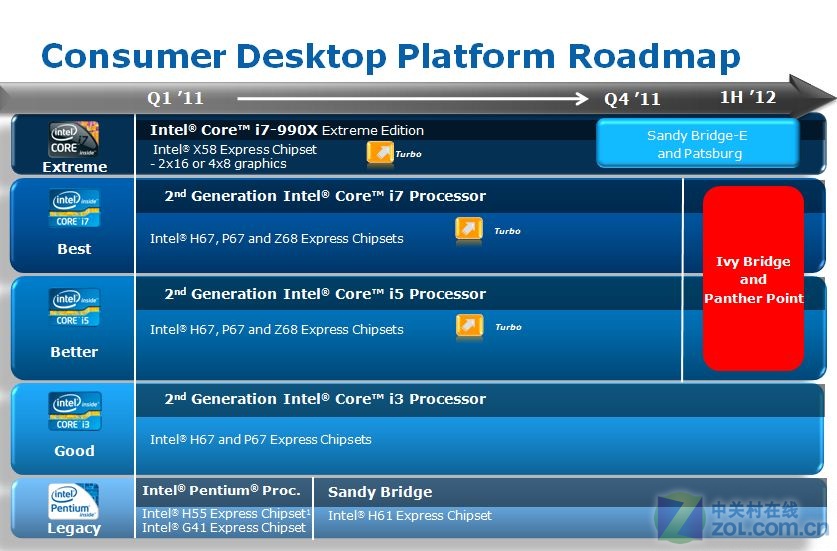
خريطة
Road Map
و فيها تظهر معالجات
Ivy Bridge
فى النصف الاول من 2012




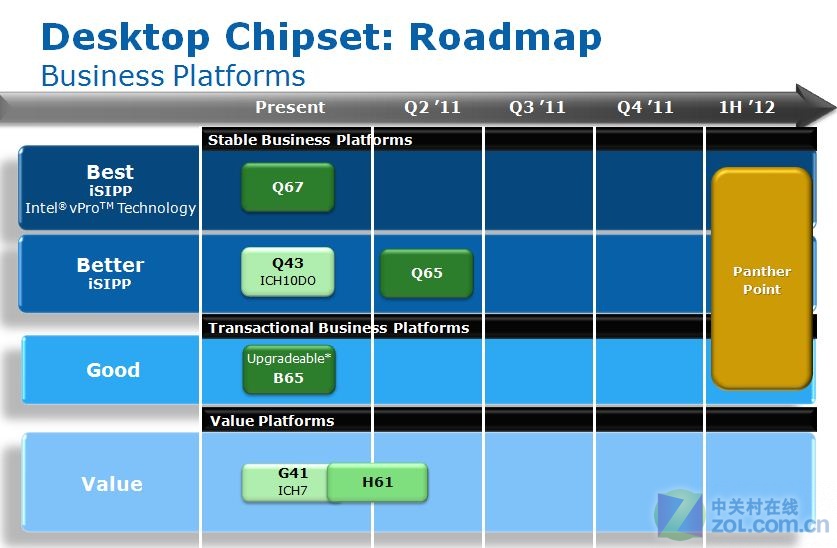
صورة هامة اخرى توضح التوافق بين
Pins
خاصة برقاقات
Sandy Bridge Cougar Point و Ivy Bridge Panther Point
و هى نقطة هام فى احتمالية توافق معالجات
Ivy Bridge
مع لوحات
Sandy Bridge
التى تستخدم نفس السوكيت
LGA 1155

صورة لمعالج
Ivy Bridge
بمميزاته

مميزات و خصائص رقاقات
Panther Point
الخاصة بمعالجات
Ivy Bridge

شرح لتقنية
Intel Rapid Storage Technology
المدعومة من معالجات
Ivy Brdige

مميزات و خصائص معالجات
Ivy Bridge
الرسومية
الخصائص الجديدة فى معالجات
Ivy Bridge
No comments:
Post a Comment